Understanding Carpentry Apprenticeship
What is a Carpentry Apprenticeship?
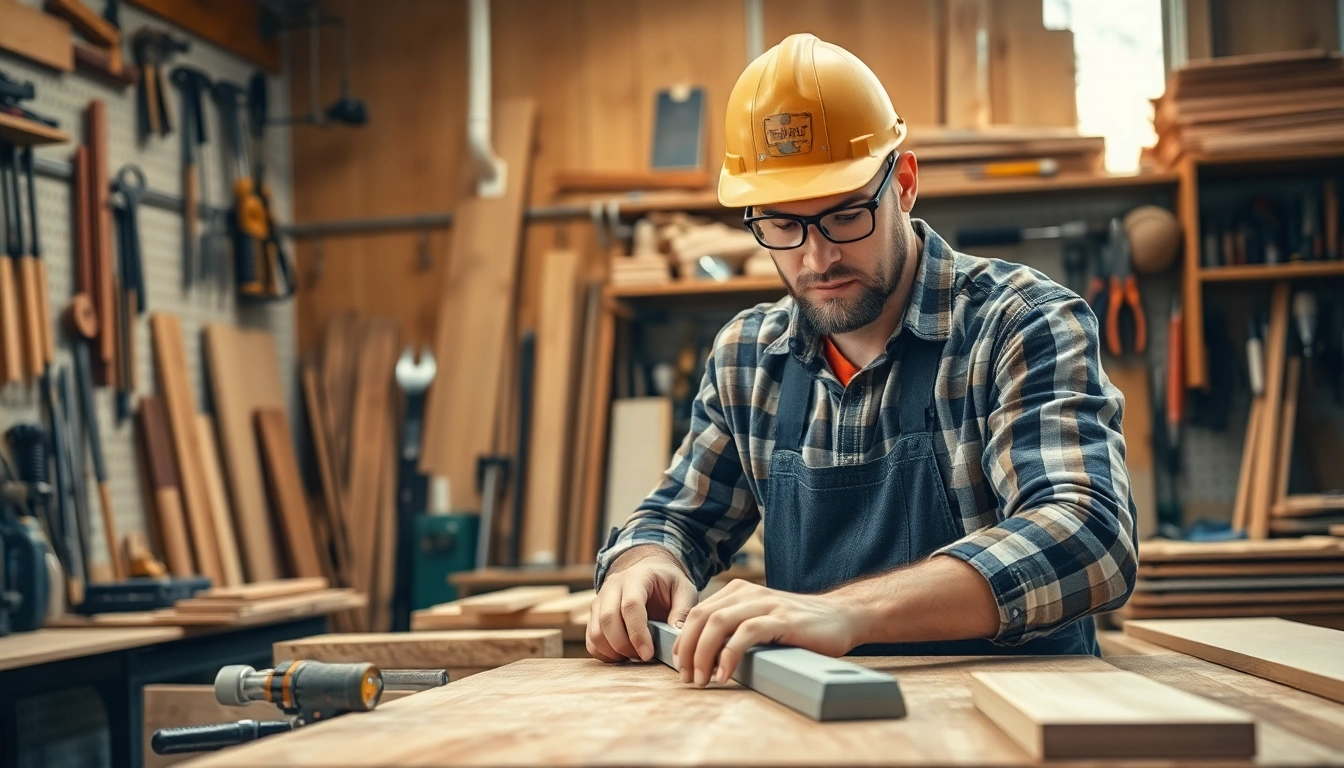
A carpentry apprenticeship is a structured training program that combines practical work experience with classroom learning to guide individuals in the art and science of carpentry. This hands-on experience offers apprentices the chance to work with experienced carpenters, gaining insights into essential carpentry techniques, safety protocols, and industry practices. Typically lasting from three to four years, these programs prepare aspiring carpenters for a versatile and rewarding career in construction.
Benefits of a Carpentry Apprenticeship
Choosing a carpentry apprenticeship presents numerous benefits, including:
- Real-world Experience: Apprentices acquire on-the-job training that prepares them for the challenges of the carpentry field.
- Earn While You Learn: Apprenticeship programs often provide a stipend, allowing participants to earn a wage while gaining invaluable skills.
- Licensure and Certification: Completing an apprenticeship can lead to licensure and certifications that enhance job prospects.
- Networking Opportunities: Working under seasoned professionals fosters connections that can serve beneficial throughout one’s career.
- Skill Diversity: Apprentices learn various skills, from framing and finishing to advanced techniques, maximizing their employability.
Who Should Consider This Path?
A carpentry apprenticeship suits various individuals, including those:
- With a passion for building and working with their hands.
- Seeking a stable career in the construction industry.
- Who prefer practical training over traditional academic paths.
- Aspiring to specialize in a particular carpentry niche such as residential, commercial, or industrial carpentry.
How to Find the Right Carpentry Apprenticeship
Researching Available Programs
The initial step in pursuing a carpentry apprenticeship involves extensive research. Prospective apprentices should look for programs that align with their career goals. Resources include local trade schools, unions, and informational websites. For a comprehensive list of programs and details on carpentry apprenticeship, individuals can start their search at carpentry apprenticeship platforms and associations.
Evaluating Program Quality
Not all apprenticeship programs are created equal. When assessing quality, consider factors such as:
- Accreditation: Ensure that the program is recognized by national or state organizations.
- Curriculum: Look for a curriculum that covers a broad range of skills and knowledge in carpentry.
- Instructor Qualifications: Research the experience and backgrounds of the instructors to judge their expertise.
- Apprentice Feedback: Reach out to former apprentices for their insights and experiences regarding the program.
Understanding Application Requirements
Application requirements can vary widely from one program to another. Typically, applicants need to provide:
- A high school diploma or equivalent.
- Proof of basic math skills.
- A resume detailing relevant experience, if any.
- References and recommendation letters.
- Proof of physical fitness, which is crucial for the demands of the job.
Essential Skills for Aspiring Carpenters
Technical Skills Development
Technical skills are at the core of effective carpentry. During an apprenticeship, individuals will learn to read blueprints, calculate measurements accurately, and master various woodworking techniques. Mastery of these skills is crucial not only for quality work but also for ensuring safety on the job site.
Tools and Equipment Knowledge
Carpenters use a wide range of tools, from hand tools to advanced machinery. Understanding how to use tools safely and effectively is vital. Apprentices should familiarize themselves with:
- Hand tools like saws, chisels, and hammers.
- Power tools such as drills, nail guns, and sanders.
- Measuring instruments including levels and tape measures.
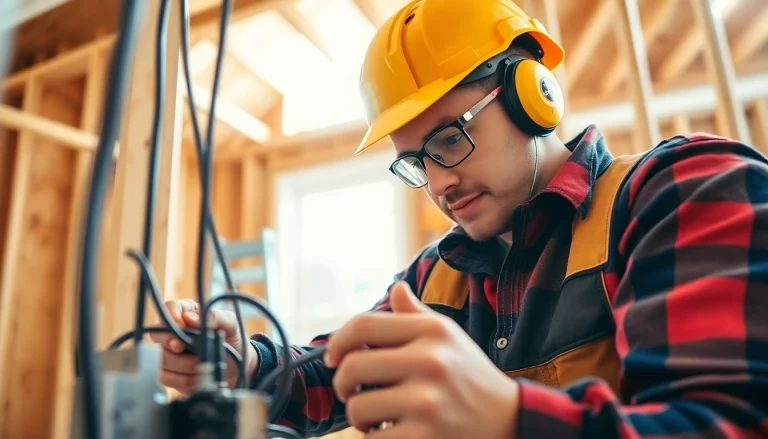
- Safety equipment, including helmets and goggles, to prevent injuries.
Safety Practices in Carpentry
Safety is paramount in carpentry. Apprentices should be diligent in following safety protocols such as keeping work areas tidy, using personal protective equipment (PPE), and adhering to guidelines when operating equipment. Understanding OSHA standards is also essential for ensuring compliance with federal safety regulations.
Challenges in Carpentry Apprenticeship
Common Obstacles and Solutions
Carpentry apprentices face several challenges, but with perseverance, they can overcome them. common obstacles include adjusting to the physical demands of the job, learning technical skills quickly, and mastering safety practices. Solutions may involve seeking mentor guidance, taking extra time for skill practice, and improving physical fitness through regular exercise.
Time Management During Training
Effective time management is crucial during an apprenticeship. With work and educational requirements, apprentices must prioritize tasks and create schedules that allow for study and skill practice. Techniques such as setting daily goals and using planners can help maintain productivity and meet program deadlines.
Overcoming Physical Demands
The physical nature of carpentry can be taxing. To manage these demands, apprentices should engage in strength training to build endurance, practice proper lifting techniques, and ensure they maintain a healthy diet to support their energy levels. Taking regular breaks while working also minimizes fatigue and reduces injury risks.
Career Paths After Carpentry Apprenticeship
Advancement Opportunities
After completing a carpentry apprenticeship, numerous career paths are available. Graduates can work as journeyperson carpenters, specializing in areas like residential construction, commercial carpenter roles, or even transitioning into management positions. With advanced skills, they also can take on roles as estimators, project managers, or inspectors.
Potential Earnings in Carpentry
The earning potential for carpenters post-apprenticeship varies based on specialization, location, and experience. On average, carpenters can make a competitive wage, with opportunities for overtime and bonuses. Skilled carpenters with significant experience in specific niches can command even higher salaries.
Continuing Education and Skills
Continuing education plays a vital role in a carpenter’s career growth. Participating in workshops, obtaining certifications in new technologies, or enrolling in specialized courses allows carpenters to stay current with industry trends and improve their skillsets, making them more marketable in an ever-evolving job landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the duration of a carpentry apprenticeship?
A typical carpentry apprenticeship lasts about three to four years, depending on the program structure and requirements.
2. Do I need prior experience to apply for an apprenticeship?
While prior experience is beneficial, it is not always necessary. Many programs accept beginners who show a willingness to learn.
3. Are carpentry apprenticeships paid?
Yes, most apprenticeships offer paid training, allowing you to earn while you learn essential skills in the field.
4. What kinds of projects do carpenters typically work on?
Carpenters work on various projects, including building homes, commercial spaces, renovating existing structures, and installing cabinetry.
5. Can I specialize in a particular area after my apprenticeship?
Absolutely! After completing an apprenticeship, you can choose to specialize in areas like framing, finishing, or even green building practices.