1. Introduction to Saltwater Fly Fishing
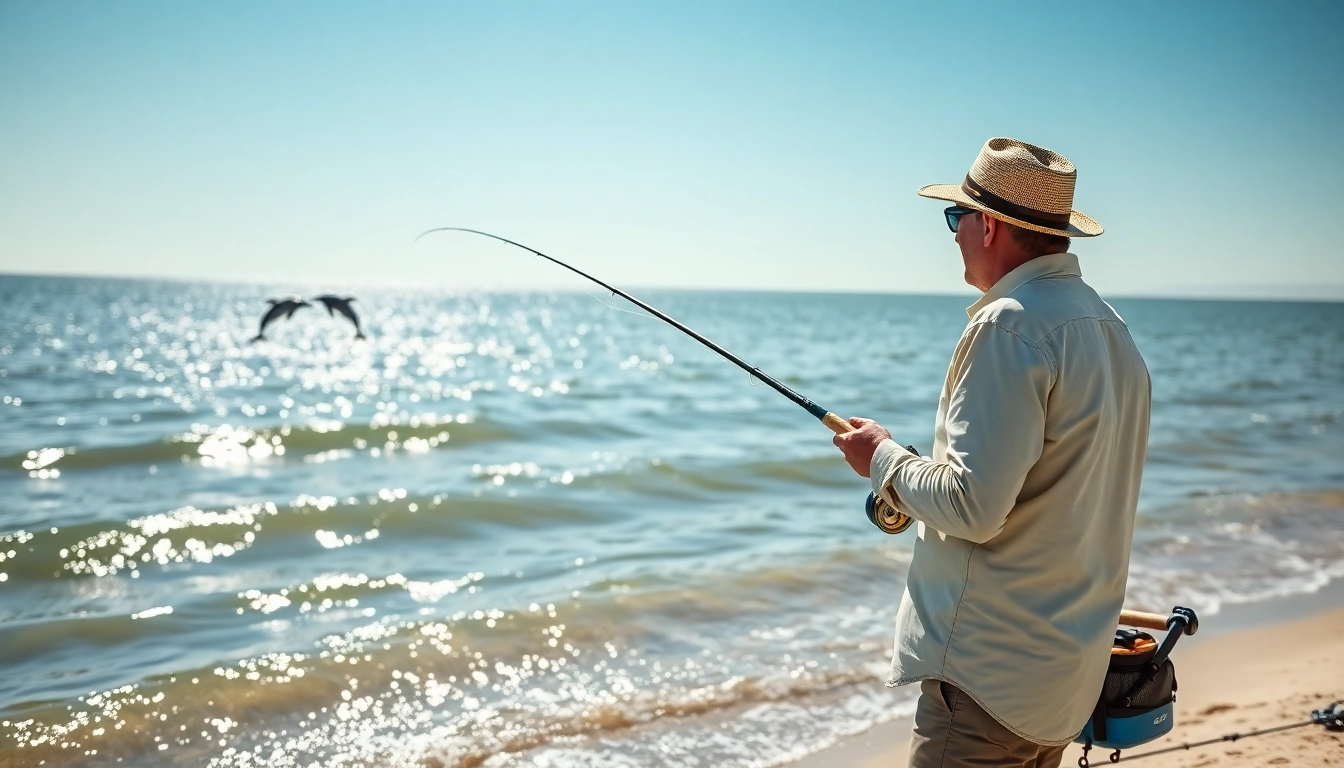
Saltwater fly fishing is an exhilarating and challenging pursuit, drawing enthusiasts from across the globe. This specialized form of fishing requires not only skill and technique but also an in-depth understanding of the unique environments and species involved in the sport. Whether you’re a seasoned angler or a novice, the joys of saltwater fly fishing can be explored through the right equipment, techniques, and best practices.
1.1 What is Saltwater Fly Fishing?
Saltwater fly fishing is the practice of catching fish in saltwater environments using a fly rod and artificial flies. Contrary to traditional fishing methods, this technique involves casting lightweight flies meant to mimic bait fish or other aquatic creatures, thereby enticing larger saltwater species. Saltwater fly fishing can take place in various locations, including beaches, reefs, estuaries, and deep sea waters, offering diverse opportunities for anglers to engage with the marine ecosystem.
1.2 Key Equipment for Success
The right equipment is crucial for a successful saltwater fly fishing experience. Here are the essential components:
- Fly Rods: Saltwater fly rods are typically longer and sturdier than freshwater rods, usually ranging from 8 to 12 feet. They are designed to cast heavier flies and withstand harsh saltwater conditions.
- Reels: Look for saltwater reels made from corrosion-resistant materials. A good reel should have a solid drag system to handle runs from larger fish.
- Lines and Leaders: Saltwater fly lines are weight-forward and designed to cast larger flies and handle strong winds. Leaders should be tapered and made from strong, abrasion-resistant materials.
- Flies: Select flies that mimic local baitfish or crustaceans. Popular patterns include Clouser Minnows, Deceivers, and EP flies.
- Gear and Accessories: Don’t forget polarized sunglasses, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunscreen to protect against the elements.
1.3 Identifying Prime Locations
Finding the right spot for saltwater fly fishing is critical. Areas rich in baitfish and nearby structures such as reefs, drop-offs, and mangroves often produce the best results. Consider the following when choosing a location:
- Estuaries and Inlets: These transitional zones between freshwater and saltwater are hotspots for various species.
- Mud Flats: Ideal for sight-fishing since the shallow water allows visibility of fish and their behavior.
- Reefs: Home to a diverse range of fish species; learn to identify the best fishing periods for each locality.
- Open Ocean: Target pelagic species such as tuna and dorado by understanding their migratory patterns.
2. Essential Techniques for Saltwater Fly Fishing
2.1 Casting Techniques in Saltwater
Effective casting is paramount in saltwater fly fishing due to wind conditions and the need for precision. Master the following techniques:
- Double Haul: This advanced casting technique increases line speed and distance. It involves pulling the line with the opposite hand while casting with your dominant hand.
- Single Handed Cast: Ideal for short to mid-range distances, the single-handed cast focuses on timing and smooth motion.
- Roll Cast: Particularly useful in windy conditions or tight spaces, the roll cast allows you to cast without a back cast.
2.2 Reading Tides and Currents
Understanding tidal patterns is another critical aspect of saltwater fly fishing. Fish often move with the tides, making it essential for anglers to time their outings appropriately. During an incoming tide, fish usually feed aggressively, whereas during an outgoing tide, they may retreat to deeper waters. Always check local tide charts and consider factors like lunar phases that can influence fish behavior.
2.3 Recognizing Fish Behavior
Successful anglers pay close attention to environmental cues and fish behavior. Look for signs such as:
- Surface Activity: Splashes, jumping fish, or diving birds indicate fish are feeding.
- Changes in Water Color: Areas of discolored water, often called “mudlines,” may indicate the presence of fish.
- Temperature Variations: Fish often congregate in warm water; using a thermometer can provide insights on where to fish.
3. Best Practices for a Successful Outing
3.1 Ethical Fishing Practices
Engaging in ethical fishing practices is essential to preserve aquatic ecosystems. Adhere to these principles:
- Catch-and-Release: Minimizing stress on fish populations by practicing catch-and-release fishing.
- Respect Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local fishing guidelines, including size and bag limits.
- Leave No Trace: Clean up your fishing area and respect wildlife habitats to maintain healthy ecosystems.
3.2 Preparing for Weather Conditions
Weather can significantly affect your fishing experience. Prepare accordingly by checking forecasts and considering:
- Wind Speed: High winds can complicate casting and diminish visibility. Plan your timing and location based on wind conditions.
- Temperature: Fish often react differently in varying temperatures; be ready to adapt your techniques accordingly.
- Storms: Avoid fishing during storms, as they pose safety risks and can alter fish behavior.
3.3 Safety Precautions While Fishing
Your safety should always be a top priority. Here are some features to consider when saltwater fly fishing:
- Wear a Personal Flotation Device: Always wear a PFD when fishing from a boat or kayak.
- Stay Hydrated: Bring adequate water and provisions to avoid dehydration.
- Check for Marine Hazards: Be aware of tides, currents, and potential hazards like jellyfish or sharp corals.
4. Tools and Tactics for Catching Saltwater Species
4.1 Top Saltwater Fish Species to Target
Different species require different approaches and techniques. Here are some of the most sought-after saltwater species by anglers:
- Bonefish: Known as the “ghosts of the flats” for their stealth and elusiveness.
- Permit: Highly prized for their challenging behavior and delicious taste.
- Tarpon: Lauded for their size and incredible leaps when hooked.
- Striped Bass: Popular in both freshwater and saltwater, they offer great fighting capability.
4.2 Effective Flies and Lures
Choosing the right flies and lures can make or break a successful fishing trip. Some effective options include:
- Clouser Minnow: A versatile fly that can mimic various baitfish effectively.
- Deceiver Patterns: Designed to appear as an injured baitfish, enhancing their enticement.
- Crab Flies: Particularly effective when targeting species like permit, as crabs are a primary food source.
4.3 Seasonal Strategies for Different Species
Understanding seasonal patterns can greatly increase your chances of success. Research the migration and spawning cycles of your target species to plan accordingly. For example:
- Spring: Focus on migrating species like striped bass as they return to spawn.
- Summer: Hunt for tarpon and permit in backcountry areas and near reefs.
- Fall: Target migrations for various species, as fish often feed heavily before winter.
- Winter: Seek deeper waters for species that thrive in cooler conditions, such as some species of snapper.
5. Advanced Saltwater Fly Fishing Techniques
5.1 Fly Tying for Saltwater Fishing
Mastering fly tying can significantly enhance your effectiveness as an angler. By creating your own flies, you can tailor designs that mimic local bait effectively. Key techniques include:
- Material Selection: Utilize strong, durable materials that can withstand the wear and tear of saltwater environments.
- Color Patterns: Experiment with color variations to match local forage and enhance visibility in the water.
- Size Variations: Experiment with different sizes to see what works best in varying conditions and for different species.
5.2 Fishing in Challenging Conditions
Adverse conditions can often test an angler’s skills. Developing techniques for challenging scenarios, such as poor visibility, high winds, or strong currents, can lead to success. Strategies include:
- Adjust Your Casting Angle: Find an optimal angle that allows for better wind resistance and control.
- Use Heavier Flies: A heavier fly can penetrate strong currents and maintain better casting distance.
- Focus on Low-Light Conditions: Early mornings or late evenings often yield better results when fish are actively feeding.
5.3 Tracking and Finding Fish Schools
Being able to locate and track schools of fish is vital in saltwater fly fishing. Employ these practices to enhance your spotting skills:
- Use Binoculars: Helps increase your field of vision and allows for spotting fish activity from afar.
- Look for Surface Disturbances: Pay attention to splashes, nervous water, and diving birds to seek out feeding schools.
- Maintain Constant Movement: Moving around to scout different locations can increase your chances of coming across fish.