Understanding On-Site Videography
Definition and Key Concepts of On-Site Videography
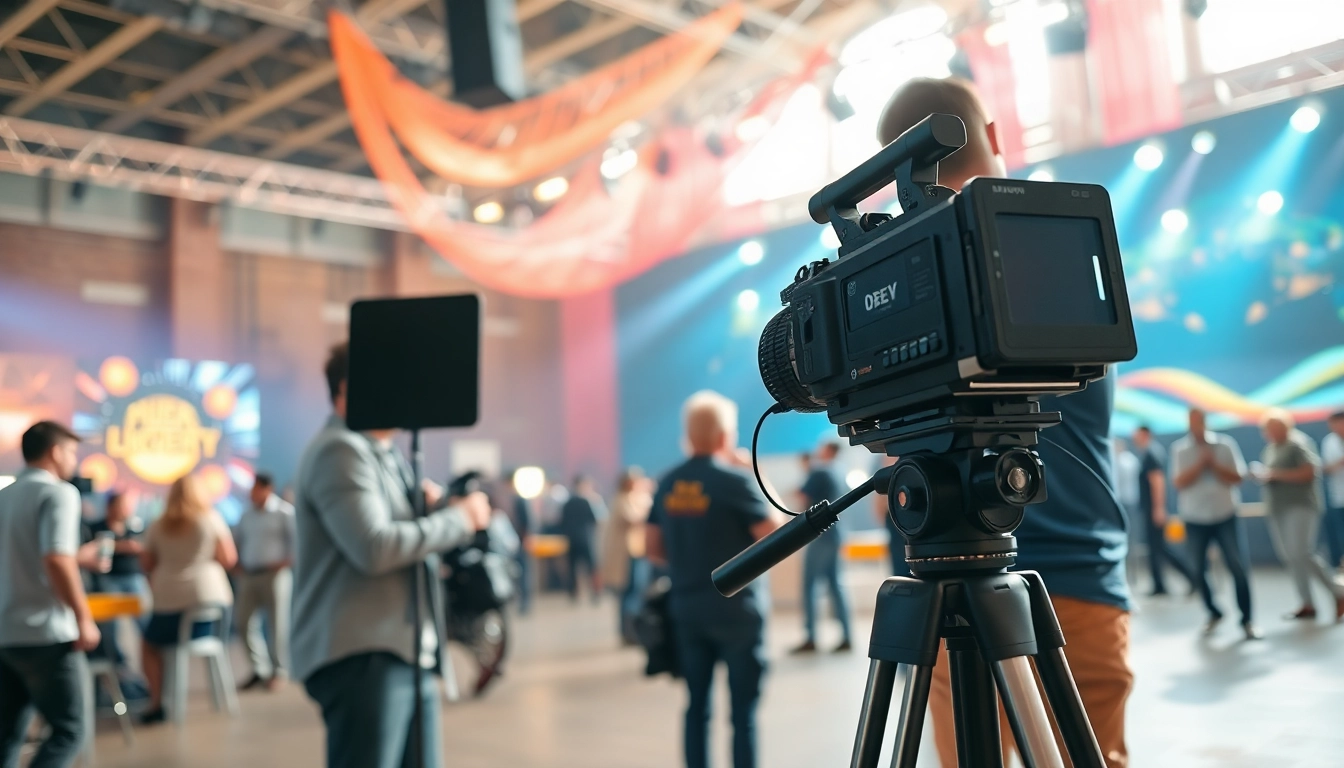
On-site videography refers to the capturing of video footage at a particular location relevant to the subject matter. Unlike traditional studio production, on-site videography allows for the incorporation of authentic environments, enabling the content to resonate more meaningfully with audiences. This method leverages the natural setting, providing context and depth to the video narrative.
At its core, on-site videography entails planning, location scouting, video production, and post-production processes, all executed at a predetermined location. This approach is particularly beneficial for scenarios requiring real-life contexts, such as events, corporate training, or promotional campaigns. The resulting footage not only serves functional purposes but also helps in creating engaging and emotionally impactful storytelling.
Benefits of On-Site Videography for Your Projects
Employing on-site videography brings numerous advantages, making it a popular choice among content creators. Here are some notable benefits:
- Authenticity: Capturing video in its natural environment heightens the authenticity of the content, allowing for genuine storytelling.
- Engagement: Viewers are more likely to connect with visual narratives set in real-world settings that they can relate to.
- Flexibility: On-site videography provides the flexibility to adjust filming techniques based on environmental conditions, enhancing creativity and visuals.
- Thematic Relevance: By shooting in locations pertinent to the content, the narrative becomes more cohesive and relevant to the intended message.
- Improved Content Variety: The diversity of environments allows videographers to experiment with different angles, light conditions, and backdrops, enriching the final product.
Common Scenarios for On-Site Videography Usage
On-site videography is utilized across various scenarios. Here are some common applications:
- Corporate Events: Capturing conferences, workshops, or company retreats, providing essential content for marketing and internal communication.
- Training and Educational Purposes: Documenting instructional sessions to create training materials or e-learning content.
- Product Demos: Showcasing products in their use environment, enhancing customer understanding and engagement.
- Event Coverage: Documenting special events such as weddings, parties, or community gatherings for personal keepsakes or client portfolios.
- Promotional Content: Creating engaging marketing materials for brands, highlighting key messages in authentic scenarios.
Planning an On-Site Videography Shoot
Choosing the Right Location for On-Site Videography
Selecting an appropriate location is fundamental to the success of on-site videography. The location should align with the project goals and theme. Consider variables such as:
- Relevance: Ensure the location resonates with the subject matter to enhance the narrative.
- Accessibility: Assess the ease of access for the production crew and participants.
- Aesthetics: Evaluate whether the environment’s visual appeal will contribute positively to the video.
- Noise and Light Conditions: Identify potential distractions and lighting issues that could affect the audio and visual quality.
Conducting a location scout before shooting can unveil insights that improve planning and execution. Photographs taken during scouting can also guide the videographers regarding shooting angles and the potential for creative shots.
Essential Equipment for On-Site Videography
Successful on-site videography hinges on the right equipment. The following tools are essential:
- Camera: A high-quality camera, preferably capable of capturing at least 1080p video for sharp, professional-quality footage.
- Tripod: Stable footage is crucial, so incorporating a sturdy tripod helps minimize camera shake.
- Microphones: High-quality audio is just as important as video. Use lavalier or shotgun microphones to capture clear sound.
- Lighting Equipment: Portable LED lights can greatly enhance video quality when natural light is insufficient.
- Editing Software: Post-production editing software allows for refining the footage, adding effects, and ensuring a polished final product.
Creating a Comprehensive Shoot Schedule
A well-structured shoot schedule is essential for maintaining organization and maximizing efficiency during production. Your schedule should encompass:
- Timeline: Define specific shoot dates and hours for each location, allowing for adequate time for setups and adjustments.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign clear roles to each team member from videographers to sound technicians to streamline processes.
- Shooting Order: Organize the shoots based on location to minimize downtime and make logistics practical.
- Contingency Plans: Always prepare for potential issues such as bad weather or equipment failures by having backup plans in place.
Best Practices for On-Site Videography
Engaging the Audience During On-Site Videography
To create captivating on-site videography, engaging your audience is key. Apply these strategies to boost viewer engagement:
- Tell a Story: Frame the content within a compelling narrative structure to hold the audience’s attention.
- Incorporate Testimonials: Leverage authentic voices within the footage to create relatability and build trust.
- Dynamic Editing: Use varied editing techniques, including jump cuts and montages, to keep the pace lively and engaging.
- Direct Interaction: Engage directly with the audience through on-screen questions or prompts to encourage viewer participation.
Techniques to Enhance Video Quality
To achieve the highest quality in your on-site videography, consider the following techniques:
- Sound Checks: Conduct thorough audio checks before shooting to ensure clarity and absence of background noise.
- Experiment with Angles: Utilize various angles to capture interesting perspectives, making the content visually rich.
- Proper Framing: Ensure subjects are well-framed and that the background complements the visual narrative.
- Consistent Lighting: Always be mindful of changing lighting conditions; adjust accordingly using reflectors or additional lights.
Post-Production Tips for On-Site Videography
The post-production phase is crucial for refining your on-site videography. Here are key post-production practices:
- Editing: Cut out any unnecessary footage to maintain pacing. Use software to add graphics, titles, and transitions that enhance the narrative.
- Color Grading: Color correction and grading can drastically improve the mood and tone of the video.
- Audio Enhancement: Balance audio levels, add background music, and incorporate sound effects to enrich the viewing experience.
- Feedback Loops: Share drafts with stakeholders for feedback before finalizing; iterative reviews can improve the quality of the final output.
Case Studies of Successful On-Site Videography
Event Documentation: Success Stories
There are numerous success stories that showcase how on-site videography can effectively document events:
For instance, documenting a corporate event can deliver significant value in enhancing brand presence. Filming testimonials during the event can provide social proof and reinforce the company’s mission to clients and customers. Properly edited, these videos can be used in various marketing channels, amplifying their impact.
Corporate Training and Educational Uses
On-site videography serves as an invaluable tool in corporate training. By capturing training sessions, companies can provide persistent learning resources for employees. For example, an organization might film a workshop, capturing the most effective methods presented by trainers, which can be reviewed by employees at their own pace.
Creative Marketing Campaigns through On-Site Videography
Creative marketing campaigns benefit immensely from on-site videography. Utilizing real-world contexts for product launches, companies can create impactful ads that humanize their brands. For instance, a cooking brand might capture chefs in their kitchens preparing meals using their products, effectively inspiring and engaging potential customers.
Measuring the Impact of On-Site Videography
Analyzing Viewer Engagement and Feedback
Measuring the effectiveness of on-site videography requires systematic analysis of viewer interactions and feedback. Use indicators such as:
- View Count: Evaluate how many views your videos garner across platforms.
- User Engagement: Monitor likes, shares, and comments to gauge audience interest.
- Watch Time: Analyze average watch times to understand viewer retention and interest.
- Feedback Surveys: Conduct surveys to gain direct insights from viewers regarding their perceptions and interests.
Understanding the ROI of On-Site Videography
Determining the return on investment (ROI) for on-site videography involves assessing both tangible and intangible benefits. Considerations include:
- Cost Savings: Evaluate how the efficiency of on-site shoots saves production time and costs.
- Lead Generation: Analyze how effective videos contribute to increased inquiries and sales.
- Brand Awareness: Assess growth in brand recognition through the audience reach of video content.
- Content Longevity: Recognize that well-produced videos have long-lasting value and can be used for years to come.
Future Trends in On-Site Videography
As technology and audience preferences evolve, so does the landscape of on-site videography. Anticipate the following trends:
- Live Streaming: Growing demand for live broadcasts of events will integrate real-time audience engagement.
- 360-Degree Videos: Immersive video experiences are gaining traction, allowing audiences to explore environments actively.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Integration of AR in videos will soon become a norm, enhancing viewer interaction.
- Drone Videography: Aerial shoots will continue to expand on-site videography, providing unique perspectives not possible through traditional means.